HISTORY
 Egyptian reliefs from 1500BC depict siphons used to extract liquids from large storage jars.There is physical evidence for the use of siphons by Greek engineers in the 3rd century BC at Pergamon.
Egyptian reliefs from 1500BC depict siphons used to extract liquids from large storage jars.There is physical evidence for the use of siphons by Greek engineers in the 3rd century BC at Pergamon.Hero of Alexandria wrote extensively about siphons in the treatise Pneumatica.In the 9th century,the Banu Musa brothers invented a double-concentric siphons,which they described in their Book of Ingenious Devices.
Siphons were studied further in the 17th century,in the context of suction pumps
OPERATIONS
There are two main issues in the operation of a siphon:
-> Why liquid flows from the higher reservoir to the lower
reservoir,which is basic;and
-> Why liquid flows up the siphon,which is subtler.
The first issue is basic : liquid flows from the higher level to
the lower level because the lower location has lower Potential
energy.This is independent of the particular connection-liquids
will also flow from higher to lower if there is a direct path,or
if there is a tube that goes below the reservoirs,and these do
not depend on siphon effect.
The second issue,why liquid flows up,is due primarily to
atmospheric pressure,and is the same mechanism as in
Suction pumps,Vaccum pumps and barometer,and can
be replicated in the simple experiment of placing a straw
in water,capping the top,and pulling it up.
THEORY/operating principle
A siphon works because gravity pulling down on the taller
column of liquid causes reduced pressure at the top of the
siphon.In more detail,one can look at how the hydrostatic
pressure varies through the siphon,considering in turn the
vertical tube from the bottom reservoir,and the horizontal
tube connecting them.At liquid level in the top reservoir,the
liquid is under atmospheric pressure,and as one goes up the
siphon,the hydrostatic pressure decreases.The hydrostatic
pressure at the top of the tube is lower than the atmospheric
pressure by an amount proportional to the height of the tube.
Doing the same analysis on the tube rising from the
lower reservoir yields the pressure at the top of that tube;this
pressure is lower because the tube is longer,and requires that the
lower reservoir is lower than the upper reservoir,or more generally
that the discharge outlet simply be lower than the surfaces of the
upper reservoir.
SIPHON COFFEE
While if both ends of a siphon are at atmospheric pressure, liquid
flows from high to low, if the bottom end of a siphon is pressurized,
liquid can flow from low to high. If pressure is removed from the bottom
end, the liquid flow will reverse, illustrating that it is pressure driving
the siphon. An everyday illustration of this is the siphon coffee
brewer,which works as follows
->The bottom vessel is then heated; as the temperature increases, the
vapor pressure of the water increases (if a glass vessel is filled with
water, then corked (so air-tight) with a siphon sticking vertically upwards.
->Another glass vessel is placed on top, open to the atmosphere – the
top vessel is empty, the bottom is filled with water.
->Increasingly evaporates); when the water boils the vapor pressure
equals atmospheric pressure, and as the temperature increases above
boiling the pressure in the bottom vessel then exceeds atmospheric
pressure, and pushes the water up the siphon tube into the upper vessel.
->A small amount of still hot water and steam remain in the bottom vessel
and are kept heated, with this pressure keeping the water in the upper
vessel.
->when the heat is removed from the bottom vessel, the vapor
pressure decreases, and can no longer support the column of
water – gravity (acting on the water) and atmospheric pressure
then push the water back into the bottom vessel.
APPLICATION
1.When certain liquids are needs to be purified,siphoning can help to
prevent either the bottom or the top from being transferred out of
one container into a new container.
2.Siphoning is thus useful in the fermentation of wine and beer for
this reason: since it can keep unwanted impurities out of the new
container.
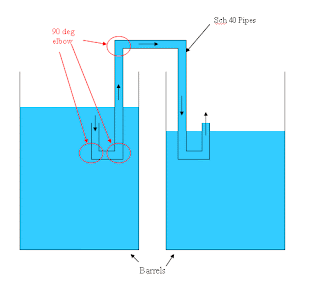
3.Siphoning is common in irrigated fields to transfer a controlled amount
of water from a ditch,into furrows.
4.Self-constructed siphons,made of pipes or tubes,can be used to
evacuate water from cellars after floodings.
5.Large siphons may be used in municipal waterwork and Industry.
The siphon may be primed by closing the intake and outlets and
filling the siphon at the crest.If intakes and outlets are submerged,
a vaccum pump may be applied at the crest to prime the siphon.
SIPHON USED AS !
BOWL SIPHON:- Bowl siphons are part of Flush toilets.Siphon action
in the Bowl siphons out the contents of the toilet bowl and creates
the characteristic toilet "sucking" sound.
Some toilets also use the siphon principle to obtain
the actual flush from the cistern.The advantage of this system was
that no water would leak from the cistern excepting when flushed.
INVERTED SIPHON:-An inverted siphon is not a siphon but a term
applied to pipes that must dip below an obstruction to form a "U"
shaped flow path.It are commonly called Traps for their function in
preventing smelly sewer gases.Large inverted siphonsare used to
convey water being carried in canals or flumes across valleys,for
irrigation or goldmining.
BACK SIPHONAGE:- Back siphonage is a plumbing term applied to
clean water pipes that connect directly into a reservoir without an
air gap.As water is delivered to other areas of the plumbing system
at a lower level,the siphon water back out of the reservoir.
Back siphonage is a result of liquids at a lower level
drawing water from a higher level. Backflow is driven entirely by
pressure in the reservoir itself and cannot occur through an
intermediate high point.. Back siphonage can flow through an
intermediate high-point and is thus much more difficult to guard
against.
ANTI-SIPHON VALVE:-Anti-siphon valves are required in such design.
Buildings codes often contains specific sections on back siphonage
and especially for external faucets An anti-siphon valve is also required
here to prevent pressure drops in the water supply line from siphoning
water out of the toilet tank and contaminating the water system.Anti-siphon
valves function as a one-direction check valve.
Anti-siphon valves are also used medically.Note
that the anti-siphon valve in medical shunts is preventing excess
forward flow of liquid. In plumbing systems, the anti-siphon valve is
preventing backflow.
OTHER ANTI-SIPHONING DEVICES:- Along with anti-siphoning valve,
anti-siphoning devices also exit. The two are unrelated in application.
Siphoning can be used to remove fuel from Tanks.The anti-siphon
device prevents thieves from inserting a tube into the fuel .
SIPHON BAROMETER:-A siphon barometer is the term sometimes
applied to the simplest of mercury barometers. A continuous U-shaped
tube of the same diameter throughout is sealed on one end and
filled with mercury.The term "siphon" is used because the same
principle of atmospheric pressure acting on a fluid is applied.
The difference in height of the fluid between the two arms
of the U-shaped tube is the same as the maximum intermediate height
of a siphon. When used to measure pressures other than atmospheric
pressure,a siphon barometer is sometimes called a siphon gauge and not to
be confused with a siphon rain gauge. Siphon pressure gauges are
rarely used today.
SIPHON BOTTLE:-A siphon bottle is a pressurized bottle with a vent
and a valve. Pressure within the bottle drives the liquid up and out
a tube. It is a siphon in the sense that pressure drives the liquid
through a tube. A special form was the gasogene.
SIPHON CUP:-A siphon cup is the reservoir of paint attached to a
spray gun. This is to distinguish it from gravity-fed reservoirs. An
archaic use of the term is a cup of oil in which the oil is siphoned
out of the cup via a cotton wick or tube to a surface to be lubricated.
SIPHON RAIN GAUGE:-A siphon rain gauge is a rain gauge that
can record rainfall over an extended period. A siphon is used to
automatically empty the gauge. It is often simply called a
"siphon gauge" and is not to be confused with a siphon pressure
gauge.
Heron's siphon:-Heron's siphon is a siphon that works on positive
air pressure and at first glance appears to be a perpetual motion
machine. In a slightly differently configuration, it is also known as
Heron's fountain.
Venturi siphon:-A venturi siphon, also known as an eductor.It is
essentially a venturi which is designed to greatly speed up the fluid
flowing in a pipe such that an inlet port located at the throat of the
venturi can be used to siphon another fluid. See pressure head.
Siphonic roof drainage:-Siphonic roof drainage makes use of the siphoning
principle to carry water horizontally from multiple roof drains to a single
downpipe and to increase flow velocity. One benefit to this drainage technique is the reduction in required pipe diameter to
drain a given roof surface area, up to half the size. Another benefit is the
elimination of pipe pitch or gradient required for conventional roof drainage
piping.
Siphon spillway:-A siphon spillway in a dam uses the siphon effect to
increase the flow rate. A normal spillway flow is pressurized by the height
of the reservoir above the spillway whereas a siphon flow rate is governed
by the difference in height of the inlet and outlet.
Categories:
Fluid mechanics and Aero dynamics,
mechanical